- Votre santé, notre crédo !
- + 33 (0)1.45.10.18.04
- + 33 (0)7.66.12.97.17
- contact@evadeopro.fr

Infantile congenital malformations
2 août 2019
DREPANOCYTOSIS: the most common genetic disease
6 septembre 2019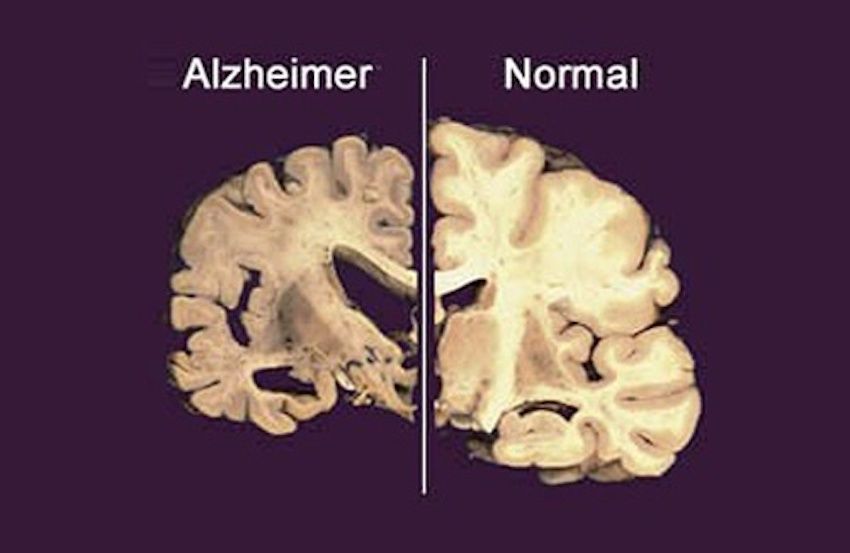
A neurodegenerative disease that manifests itself as dementia resulting from progressive damage to the central nervous system. Although it was described a hundred and ten years ago by the German neurologist Alois Alzheimer, its causes are still being debated… and unfortunately the World Health Organization estimates that 50 million people are affected by a form of dementia, of which Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form (60 to 70% of cases), representing an annual cost of approximately 850 billion euros worldwide, or more than 1% of the global GDP and a sum that should double by 2030! This neurodegenerative disorder has become a major public health issue, linked to the aging of the population.
Beyond the suffering of patients, who lose their memory and intellectual faculties, Al-zheimer also has direct consequences for their loved ones, with 63% of patients living at home. According to a study on the elderly and dependency, the « Paquid », only 28% of people with early stage Alzheimer’s disease live alone, the others benefit from the presence of a caregiver, family or professional.
A complaint about repeated omissions interfering with daily life must be alerted and formalized with a doctor: it is indeed essential to make a diagnosis as soon as possible. This is based first on the history of the disorders, then on cognitive function tests. They make it possible to evaluate the nature and severity of the disorders (memory loss, spatial and temporal orientation, performance functions, etc.) and the search for behavioural and mood disorders. Brain imaging also contributes to diagnosis, including at an early stage. MRI can exclude other causes and may reveal brain abnormalities associated with disease: a reduction in brain volume, especially in the posterior regions, and atrophy of the hippocampus are arguments in favour of a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. The use of PET gives access to other brain regions such as the temporal-parieto-occipital crossroads and the precunaeus. To reinforce the diagnosis, biological markers can help confirm the origin of symptoms. It is now possible to measure three markers of the disease in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), accessible through a lumbar puncture: amyloid beta protein, tau protein and phosphorylated tau protein.
These examinations sometimes make it possible to evoke the diagnosis of other degenerative pathologies (frontotemporal degeneration, Lewy body diseases, etc.) or vascular diseases that may mimic Alzheimer’s disease.
Unfortunately, Alzheimer’s disease cannot be cured, but appropriate management can slow its progression and improve the lives of the patient and his or her family and friends.
EVADEO PRO in partnership with many specialists is able to assist you in the diagnosis of this pathology. We assist you in your care journey as part of a complete health check-up, during a medical evacuation or a medical stay.
And because Evadeô Pro appears as the leader in medical tourism in France, we also offer you to enhance your stay by selecting among our services at a preferential price, those that correspond to your desires or your needs…
Ask to be called back, or contact us by phone or email to tell us your needs; our team will do the rest!
Evadêo Pro – Leader in healthcare stays and medical tourism in France.